Database connector (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL)
Setup connection
Using database connectors, you can connect Amalia to database servers and clusters to synchronize needed tables.
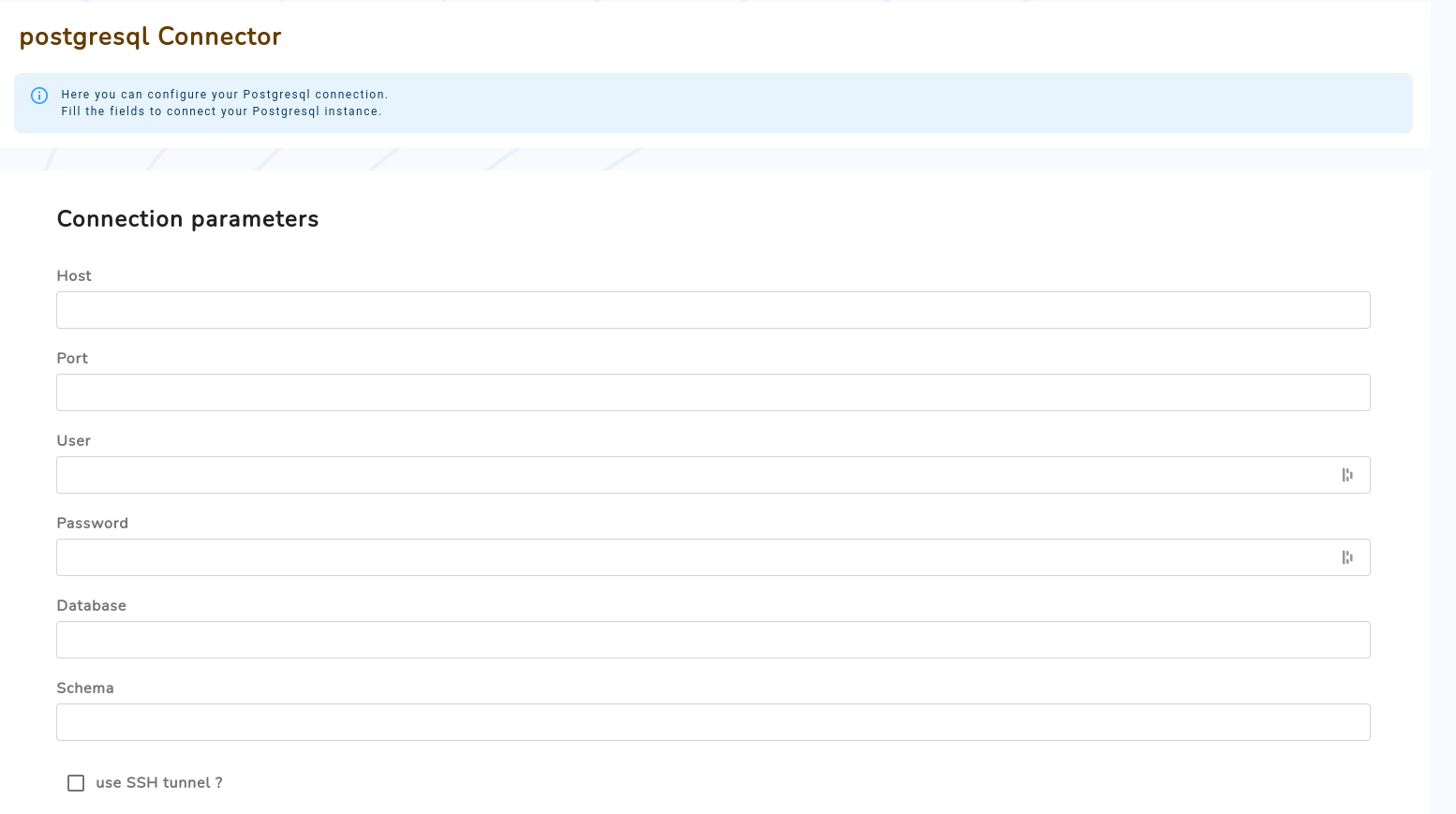
Once you click on the database connector icon, the first step will be to setup the connection to your database server. The connection is done using a "user & password" authentication, so you'll have to provide these information:
Configuration field | Description |
Host | Dns of your database server (or 127.0.0.1 in case you use SSH tunnel, see next section ) |
Port | Database server exposed port |
User | Database user with read rights on data tables you need to sync. |
Password | User's password |
Database (optional) | Database name |
Schema (optional) | Schema to connect to |
Enabling secure database access
IP address allowlist
The first step is to limit access to your data from the network layer. We recommend granting access to your database only from specific, trusted hosts.
You can ask to Amalia support to have the list of IP addresses that are needed to allow network traffic from your database cluster.
All network traffic from Amalia will come from one of the listed IP addresses. Prohibiting traffic to your database, except from these and other trusted IP addresses, is an easy way to limit data access.
Encrypted connection using SSH Tunnel
You can secure the connection to your database server using a SSH tunnel. Using a tunnel provides an encrypted connection and extra authentication for enhanced security.
Prerequisites
Before you can set up your SSH tunnel, you need to ensure that you have configured and installed SSH keys on your running environment.
SSH Tunnel configuration
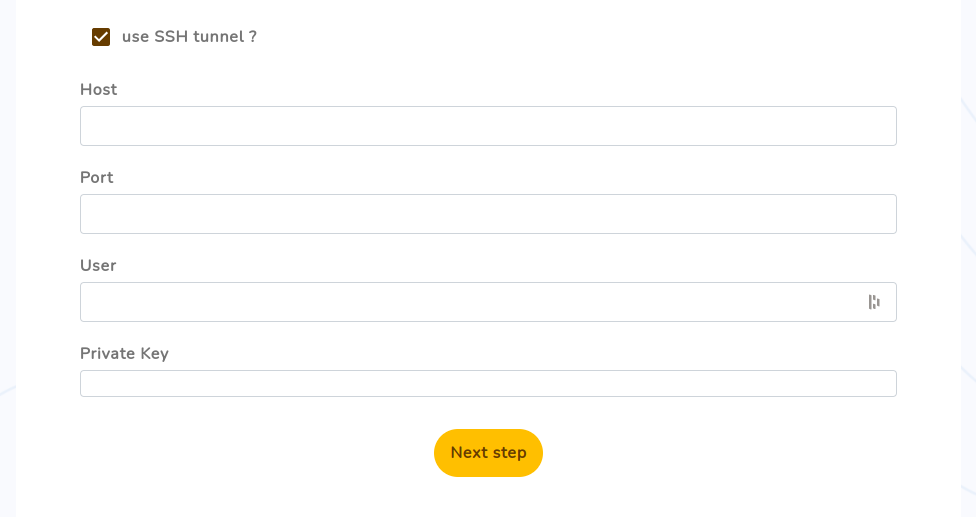
To enable database connection through SSH tunnel, you'll have to check the "use SSH tunnel ?" option and provide following information:
Configuration field | Description |
Host | Database Server host |
Port | SSH port to connect to (default is 22) |
User | SSH user |
Private key | SSH private key content |